Navigating the Digital Payment Transformation with Confidence
As Indonesia accelerates its national digital transformation, the country is building a payment system ecosystem that is both adaptive and inclusive. This transformation goes beyond the digitization of transactions—it strengthens governance, information system security, and risk management throughout the entire ecosystem.
Digital payment systems play a vital role as the backbone of a modern economy. They not only facilitate seamless and efficient financial transactions but also promote financial inclusion, enable innovation in financial services, and accelerate the growth of the digital economy. From everyday consumer purchases to complex business transactions, the reliability and integrity of digital payment systems are critical to sustaining public trust and economic momentum.
In this landscape, TÜV NORD Indonesia offers Information Technology (IT) Audit Services specifically for the Payment System sector, officially registered as an IT Audit Provider (PJA) by the Indonesian Payment System Association (ASPI). Our services help ensure that the digital payment infrastructure is secure, compliant, and resilient—supporting Indonesia’s vision for a connected and digitally empowered economy.
Payment System Ecosystem in Indonesia
Indonesia’s payment ecosystem is composed of various interconnected entities that facilitate seamless financial transactions. The key players include:
1. Payment Service Providers (PJP).
Payment Service Providers (PJP / Penyedia Jasa Pembayaran), which are banks or non-bank institutions that offer services to facilitate payment transactions for users. Bank or non-bank services such as e-wallets, card payment services, fund transfer platforms, and QR-based payment solutions.
2. Payment System Infrastructure Providers (PIP).
Payment System Infrastructure Providers (PIP / Penyelenggara Infrastruktur Sistem Pembayaran), which are entities that provide infrastructure used to transfer funds on behalf of their members. Responsible for switching, clearing, and settlement services.
3. Bank Indonesia (BI). Acts as the central regulator, setting policies, rules, and standards for the national payment system.
4. ASPI (Indonesian Payment System Association).
To ensure coordination and industry compliance, Bank Indonesia designates a Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO) in the payment system sector. The Indonesian Payment System Association (ASPI) acts as this SRO—a legally established institution that represents industry players and supports the governance and development of a reliable payment system in Indonesia. Coordinates the players in the ecosystem and sets technical guidelines such as IT audit standards.
Defined roles in Payment System Ecosystem
Each institution in the ecosystem has clear responsibilities:
- PJPs & PIPs must ensure the integrity and security of their technology systems and user data.
- Regulators oversee compliance and enforce standards.
- Audit Providers like TÜV NORD Indonesia offer Audit Services or independent assessments to ensure robust IT governance and IT risk management.
Regulation of Payment System in Indonesia
Several regulations in Indonesia related to the Payment System are governed by Bank Indonesia, which acts as the regulator and supervisor of the payment system within the jurisdiction of Indonesia. Among these regulations are the following:
- Undang-Undang No. 27 Tahun 2022 tentang Pelindungan Data Pribadi
- Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 11 Tahun 2008 tentang Informasi dan Transaksi Elektronik
- Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 19 Tahun 2016 tentang Perubahan atas Undang-Undang Nomor 11 Tahun 2008 tentang Informasi dan Transaksi Elektronik
- Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 1 Tahun 2024 tentang Perubahan Kedua atas Undang-Undang Nomor 11 Tahun 2008 tentang Informasi dan Transaksi Elektronik
- Undang-undang (UU) Nomor 4 Tahun 2023 tentang Pengembangan dan Penguatan Sektor Keuangan
- Peraturan Bank Indonesia No. 22/23/PBI/2020 tentang Sistem Pembayaran
- Peraturan Bank Indonesia No. 23/6/PBI/2021 tentang Penyedia Jasa Pembayaran
- Peraturan Bank Indonesia No. 4 tahun 2025 tentang Kebijakan Sistem Pembayaran
- Peraturan Anggota Dewan Gubernur No. 24/7/PADG/2022 tentang Penyelenggara Sistem Pembayaran oleh Penyedia Jasa Pembayaran dan Penyelenggara Infrastruktur Sistem Pembayaran PJP.
- KASPI Nomor ASPI/K-II/002/VI/2024 tentang tentang Persyaratan Pendaftaran Penyedia Jasa Audit Teknologi Informasi Dan Pengujian Keamanan
- KASPI Nomor ASPI/K-II/003/X/2024 tentang Penanganan Transaksi Transfer Antar Dana Penyelenggara Sistem Pembayaran Terhadap Rekening /Akun Pengguna Jasa Yang Terindikasi Fraud
Benefit of IT Audit on Payment System
IT Audit services provide multiple strategic advantages, including:
1. Regulatory Compliance
Demonstrates adherence to BI, OJK and ASPI policies and technical standards.
2. Enhanced Information Security
Identifies vulnerabilities and suggests mitigation measures.
3. Operational Efficiency
Assesses the effectiveness of IT processes and systems.
4. Increased Stakeholder Trust
Through independent assurance of system reliability and data protection.
5. Stronger IT Governance
With clear visibility of organizational structure, roles, responsibilities, and controls.
Content of IT Audit
TÜV NORD’s audit process covers critical domains, including:
A. IT Governance and Management
- Organizational structure and responsibilities IT strategy and policy frameworks
- Risk Management & Information Security
B. Identification and evaluation of IT risks
- Protection of information assets
- Access control and user rights management
C. IT Infrastructure and Operations
- Management of hardware, software, and networks
- Daily operations and support services
- Monitoring and reporting mechanisms
D. Application and Transaction Security
- Transaction integrity
- User authentication and authorization
- Customer data protection
E. Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity
- Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and simulations
F.Compliance Review
- Verification of implementation against regulatory and technical requirements
- Recommendations for continuous improvement
Based on PBI 22/23/PBI/2020, PBI 23/6/PBI/2021 and document requirement of PJP license by Bank Indonesia, contents of audit report are at a minimum, compliance should cover the following aspects:
A. The implementation of a technology security system that is effective and efficient while ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations, and at the very least, adheres to the following principles:
- Data confidentiality;
- System and data integrity;
- Two-factor authentication for systems and data;
- Prevention of transaction repudiation (non-repudiation); and
- System availability.
B. The existence of systems and procedures to conduct an audit trail;
C. The establishment of internal policies and procedures for the operation of information systems and human resources;
D. The fulfillment of security and reliability aspects of systems and/or networks, including those provided by third parties;
E. The existence of a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) that ensures the continuity of fund management activities. The BCP should include preventive measures and a disaster recovery plan in the event of emergencies or disruptions that render the primary system for fund management activities inoperable.
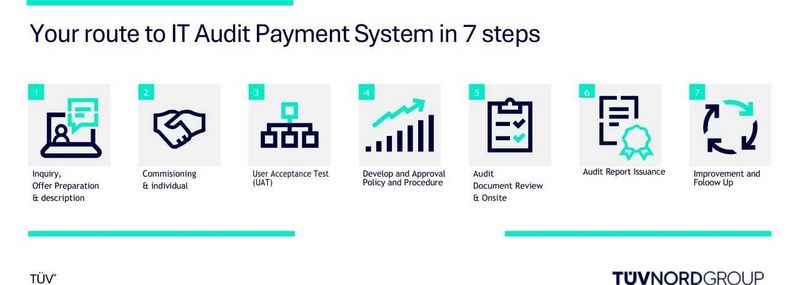
Audit procedure for IT Audit


FAQs on IT Audit
|